Using the command line interface¶
Operation of the two different modes (near real time and update modes) is done via a set of command line, which are detailed below. Every command lines have a consistent syntax and naming convention.
Every command line contains built in documentation that can be accessed by running name_of_the_cli.py --help.
Because most of the commands runs for several hours or even days, it is preferable to run them within a nohup context. See the example below.
# Run a command as a background process (allowing you to close the terminal), and writing the verbose to a log file
nohup command_name.py --arg1 input1 --arg2 input2 > ~/YYYYMMDD_processing_log.log &
Before starting¶
As detailed in the installation section, it is recommended to have installed the satmo package in a python virtual environment. Considering, you have already created a virtual environment named satmo, you have to activate that environment to be able to run a satmo command line. To activate the environment, simply run:
workon satmo
Starting satmo near real time mode¶
As detailed in the installation instruction, you probably want to start the near real time operation mode automatically as soon as the system boots up, and for that you should add and entry to the linux user crontab. However, it is of course also possible to start satmo near real time mode manually, using the satmo_nrt.py command.
Running satmo_nrt.py --help returns the following help page.
usage: satmo_nrt.py [-h] -day_vars [DAY_VARS [DAY_VARS ...]] -night_vars
[NIGHT_VARS [NIGHT_VARS ...]]
[-l1a_vars [L1A_VARS [L1A_VARS ...]]] [--no-refined]
[--no-8DAY] [--no-month] -d DATA_ROOT
[-map_res MAPPING_RESOLUTION]
[-bin_res BINNING_RESOLUTION] -north NORTH -south SOUTH
-east EAST -west WEST [-p PROJ]
[-flags [FLAGS [FLAGS ...]]] [-delay DELAY]
[-multi N_THREADS]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-day_vars [DAY_VARS [DAY_VARS ...]], --day_vars [DAY_VARS [DAY_VARS ...]]
day time variables to process
-night_vars [NIGHT_VARS [NIGHT_VARS ...]], --night_vars [NIGHT_VARS [NIGHT_VARS ...]]
night time variables to process
-l1a_vars [L1A_VARS [L1A_VARS ...]], --l1a_vars [L1A_VARS [L1A_VARS ...]]
Additional L2 variables to process from OC2 collection
(generated from L1A files)
--no-refined Disable download of refined processed L2 data,
reprocessing of L2 data from L1A, and L3m processing
from them
--no-8DAY Disable processing of 8 days temporal composites
--no-month Disable processing of monthly temporal composites
-d DATA_ROOT, --data_root DATA_ROOT
Root of the local archive
-map_res MAPPING_RESOLUTION, --mapping_resolution MAPPING_RESOLUTION
Output resolution in meters (defaults to 1000)
-bin_res BINNING_RESOLUTION, --binning_resolution BINNING_RESOLUTION
Output resolution in meters (defaults to 1000)
-north NORTH, --north NORTH
Northern boundary in DD
-south SOUTH, --south SOUTH
Southern boundary in DD
-east EAST, --east EAST
Eastern most boundary in DD
-west WEST, --west WEST
Western most boundary in DD
-p PROJ, --proj PROJ Optional Coordinate reference system of the output in
proj4 format, or any predifined crs name in seadas
l3mapgen. If None is provided, +proj=eqc +lon_0=0 is
used
-flags [FLAGS [FLAGS ...]], --flags [FLAGS [FLAGS ...]]
List of flags to use in the binning step. If not
provided defaults are retrieved for each L3 suite
independently from the satmo global variable FLAGS
-delay DELAY, --delay DELAY
NUmber of days to wait before triggering refined
reprocessing of the L2 OC2 suite from L1A
-multi N_THREADS, --n_threads N_THREADS
Number of threads to use for parallel implementation
Command Line utility to control the operational mode of the satmo system. Enables download of L2 and (day only) L1A data from OBPG server (NRT and refined processing),
processing of L3m and L2m files for several night and day variables, processing of daily composites, and processing of temporal composites. All these download and processing steps
are scheduled and ran operationally. Temporal composites are enabled by default. Use the --no-daily_compose, and --no-8DAYto disable their generation.
The L2 suite generated from L1A data by this command line is named OC2, and contains a list of variables defined in the global variable VARS_FROM_L2_SUITE. Additional variables can be
appended to the OC2 suite by passing them to --l1a_vars (these variable must have an entry in the BAND_MATH_FUNCTIONS satmo global variable). At the moment the OC2 suite is only
used for fai and afai generation, and therefore only processed up to level 2m (L2m).
------------------
Example usage:
------------------
satmo_nrt.py --day_vars chlor_a nflh sst Kd_490 --night_vars sst --l1a_vars afai fai --north 33 --south 3 --west -122 --east -72 -d /export/isilon/datos2/satmo2_data/ -multi 3
Update mode¶
Update mode is used primarilly to download and process archive data. All command start by the prefix timerange, indicating that their action apply to a range of dates defined by a --begin and --end argument. The full list of functions is presented in the table below.
| CLI name | description | Should be ran after |
|---|---|---|
timerange_download.py |
Downloads data from the OBPG servers to a local archive | None |
timerange_L2_process.py |
Generates L2 products from L1A | timerange_download.py |
timerange_L2_append.py |
Computes additional variables and appends the result to an existing L2 file | timerange_L2_process.py or timerange_download.py |
timerange_L2m_process.py |
Maps L2 product variables to a plattecarre projection | timerange_L2_process.py or timerange_download.py |
timerange_bin_map.py |
Performs spatial binning and mapping of a variable across multiple L2 files | timerange_L2_process.py or timerange_download.py |
timerange_time_compositing.py |
Perform temporal binning and mapping of a variable | timerange_bin_map.py |
timerange_daily_composite.py |
Average L3m products across different sensors | timerange_bin_map.py |
make_preview.py |
Generate png preview of a L3m file | timerange_bin_map.py or timerange_time_compositing.py |
Downloading data¶
The timerange_download.py command line can be used to download data from the OBPG servers to a local archive. It supports downloading L1A as well as L2 files, with the option to select the suite in case of L2 download, and to choose between night or day data. Running timerange_download.py --help displays the help page of the command line interface.
Warning
Downloading data for a long period without speed restriction may cause problems of breaking connection, and is not permitted during office hours at CONABIO. It is therefore preferable to limit download speed with tools like trickle. See example below.
The example below illustrates a download process (L1A data) with speed limited to 3MBps.
# Download L1A data with speed limited to 3 MB/s
nohup trickle -d 3000 timerange_download.py --terra --aqua -b 2010-01-01 -e 2012-12-31 -north 32 -south 4 -west -121 -east -73 -d /some/directory/with/free/space > YYYYMMDD_download_log.log &
Examples usage¶
- L1A data download
$ nohup timerange_download.py --terra --aqua --viirs -b 2000-02-24 -e 2016-12-31 -north 32 -south 4 -west -121 -east -73 -d /export/isilon/datos2/satmo2_data/ > ~/dl_log.log &
- L2 data download
# Ocean color variables (Blue reflectances, chlor\_a, etc)
nohup timerange_download.py --terra --aqua --viirs -b 2000-02-24 -e 2016-12-31 -north 32 -south 4 -west -121 -east -73 -p OC --no-night -d /export/isilon/datos2/satmo2_data/ > ~/dl_log.log &
# Day time SST
nohup timerange_download.py --terra --aqua --viirs -b 2000-02-24 -e 2016-12-31 -north 32 -south 4 -west -121 -east -73 -p SST --no-night -d /export/isilon/datos2/satmo2_data/ > ~/dl_log.log &
# Night time SST
nohup timerange_download.py --terra --aqua --viirs -b 2000-02-24 -e 2016-12-31 -north 32 -south 4 -west -121 -east -73 -p SST --no-day -d /export/isilon/datos2/satmo2_data/ > ~/dl_log.log &
Processing L2 data from L1A¶
The command line timerange_L2_process.py processes L2 files from L1A. The command line is a wrapper (and batcher) around the seadas utility l2gen. The figure below details the processing chain triggered by the command line.
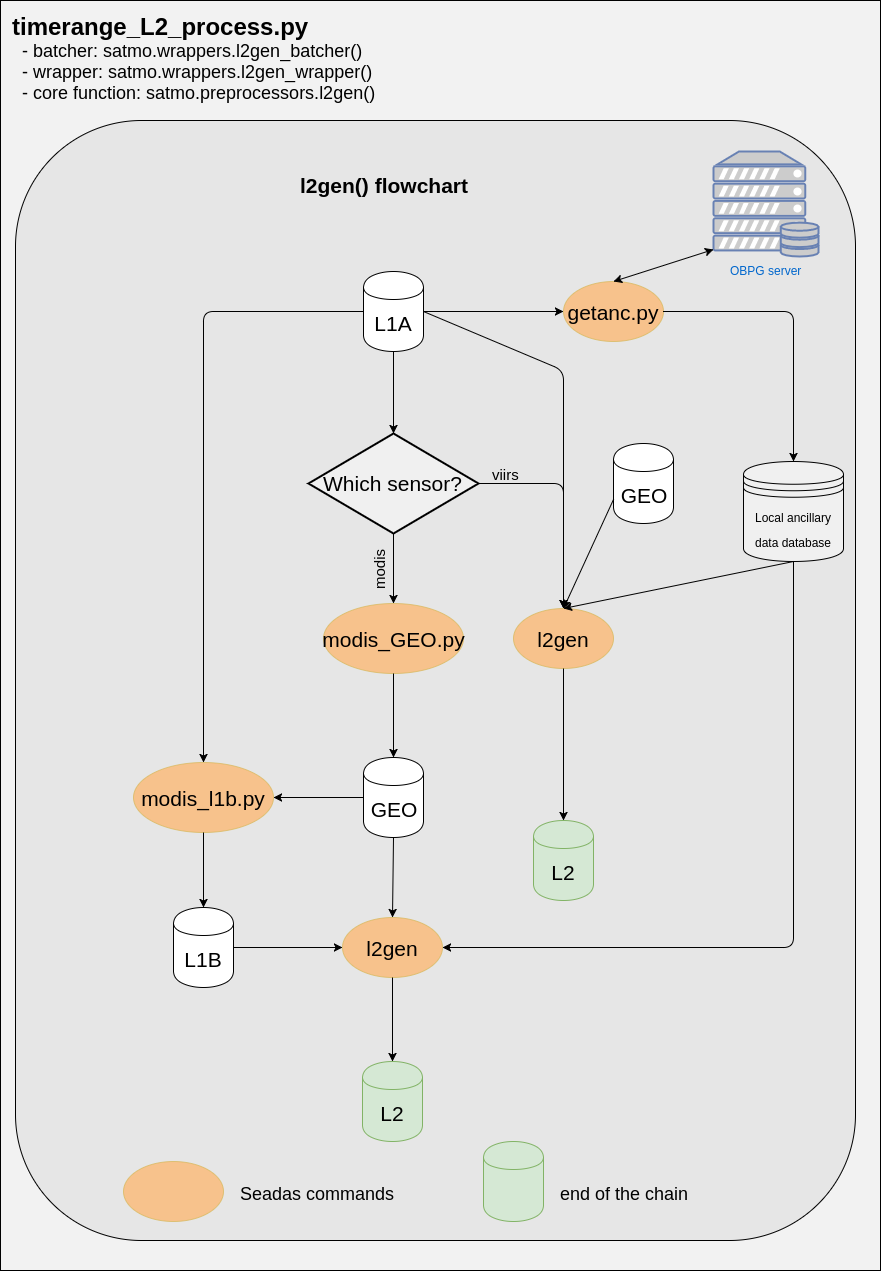
Examples usage¶
# Process a L2 suite called OC2 that contains Rayleight corrected reflectances
timerange_L2_process.py --aqua --terra --viirs -b 2014-01-01 -e 2014-12-31 -v rhos_nnn -s OC2 -d /export/isilon/data2/satmo2_data -multi 3
Generating additional L2 variables¶
The timerange_L2_append.py command line enables computing additional variables from bands present in an L2 file. The new index/band layer is appended to the L2 file from which the input were taken.
The list of variables that can be processed using that command line can be found in satmo.global_variables.BAND_MATH_FUNCTIONS. Edit that variable in the satmo source code following the existing model to enable processing of additional variables.
Examples usage¶
# Process afai and append it to the OC2 L2 suite generated by the command above
timerange_L2_append.py --aqua --terra --viirs -b 2014-01-01 -e 2014-12-31 -v afai -s OC2 -d /export/isilon/data2/satmo2_data -multi 3
Generating mapped L2 variables¶
The timerange_L2m_process.py runs seadas l2mapgen on individual L2 file, to produced mapped products.
Examples usage¶
# Process afai and append it to the OC2 L2 suite generated by the command above
timerange_L2_append.py --aqua --terra --viirs -b 2014-01-01 -e 2014-12-31 -v afai -s OC2 -d /export/isilon/data2/satmo2_data -multi 3
Generating mapped L3m variables¶
The timerange_bin_map.py runs seadas l2bin and l3mapgen sequentially, hence producing L3m products. It also produces L3b files (one for each collection), which are intermediary output in that case, but required inputs for the temporal compositing command line (timerange_time_compositing.py).
The l2bin utility uses default masking values fetched from a global variable named FLAGS and located at satmo.global_variables. Edit this variable to change the default values.
Examples usage¶
# Process chlor_a, night sst, sst, and chl_ocx for viirs, aqua and terra between 2000 and 2017
timerange_bin_map.py --aqua --terra --viirs -b 2000-01-01 -e 2017-12-31 -south 3 -north 33 -west -122 -east -72 -d /export/isilon/datos2/satmo2_data -bin_res 1 -map_res 1000 -day_vars chlor_a chl_ocx sst -night_vars sst -multi 6
Generating temporal composites¶
The timerange_time_compositing.py runs seadas l3bin and l3mapgen sequentially, hence producing mapped temporal composites.
Examples usage¶
# Generate 8 days composites for aqua, viirs and terra for the period 2000-2017 (for chlor_a, chl_ocx, sst and night sst)
timerange_time_compositing.py --aqua --terra --viirs -b 2000-01-01 -e 2017-12-31 -delta 8 -day_vars chlor_a chl_ocx sst -night_vars sst -north 33 -south 3 -west -122 -east -72 -d /export/isilon/datos2/satmo2_data
Data visualization¶
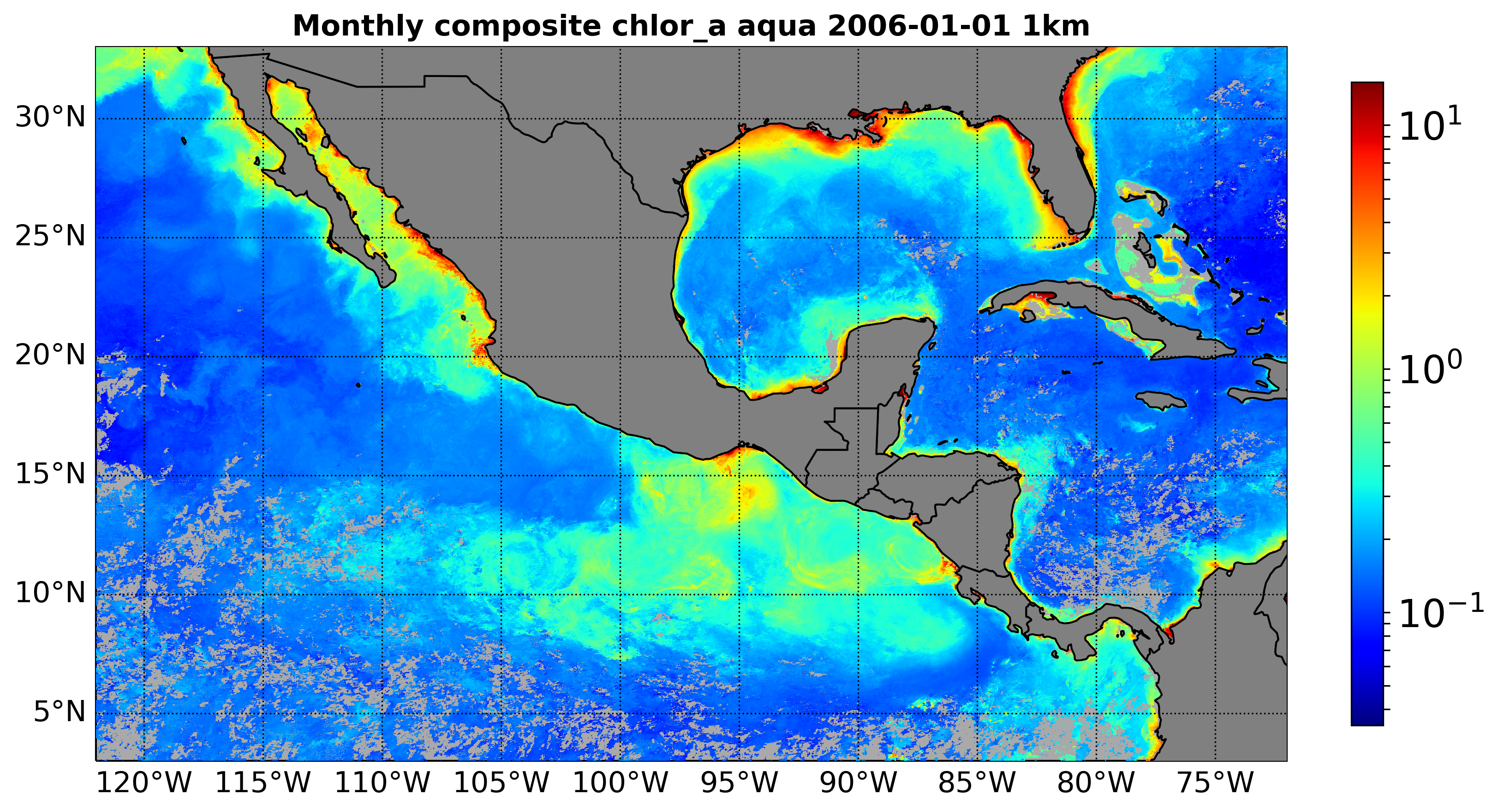
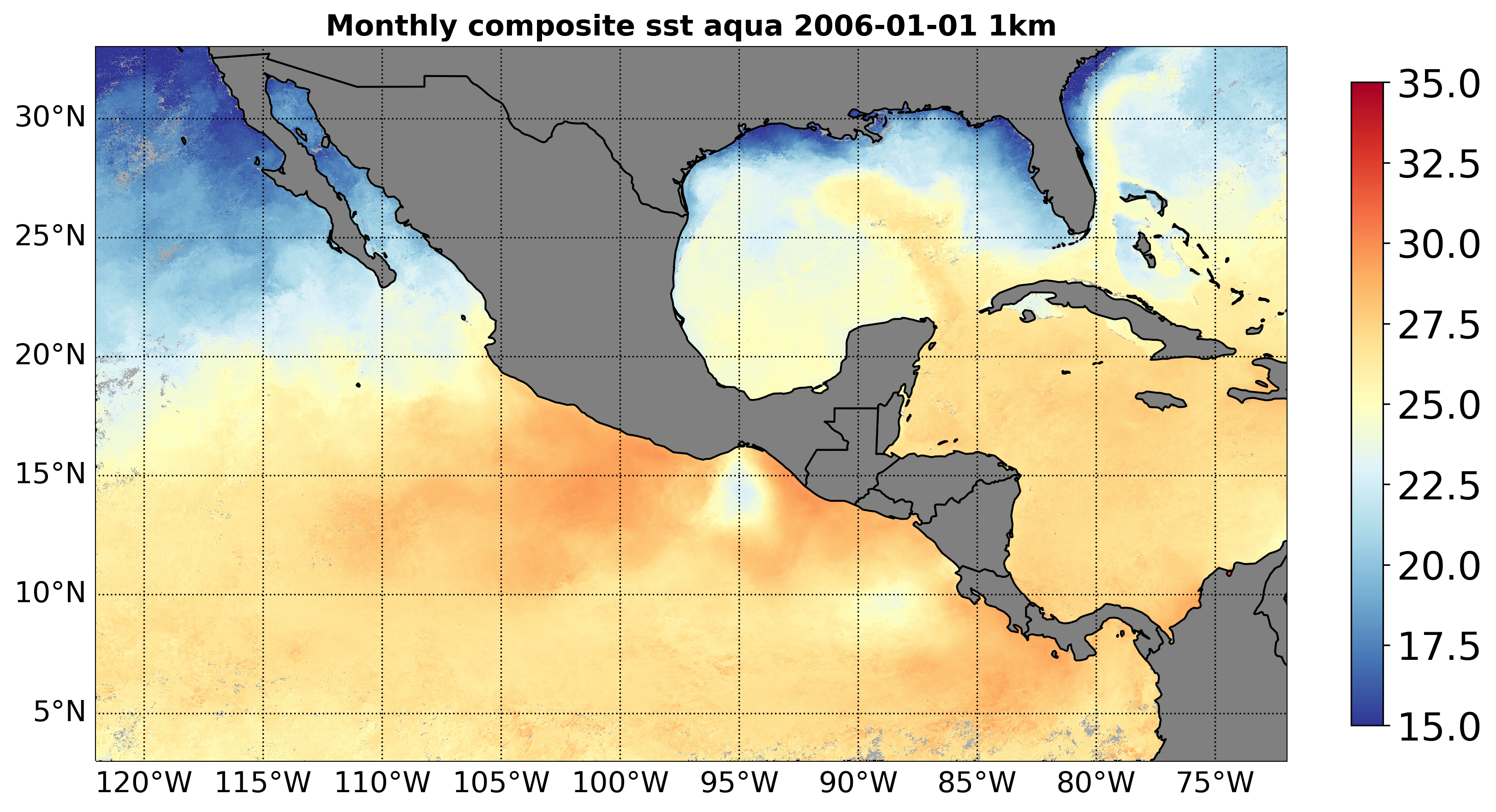
Satmo comes with a command line for generating preview of existing georeferenced tiff files. It produces png files, with continents and coastlines, and supports linear as well as logarithmic scaling of the variable. Variables have to be referenced in the global variable VIZ_PARAMS, located at satmo.global_variables. Do not set vmin to zero for a log scaled variable since the logarithm of zero is not defined.
The example below produces the figure at the end of this page.
make_preview.py A2006001.L3m_MO_CHL_chlor_a_1km.tif
make_preview.py A2006001.L3m_MO_SST_sst_1km.tif
Combinining command lines¶
It is possible to combine various steps of the processing by adding the individual command to a bash script, and runnning the script. Such example of script is available here (also pasted below). This particular example processes, from L2, for the year 2015, five variables (chlor_a nflh Kd_490 sst nsst) to level 3, including 8 days composites and monthly composites.
The different steps to run such script are to:
- Save the script not forgetting the bash shebang
- Make the script executable
- Run the script with a command like
nohup ./script_name.sh > ~/YYYYMMDD_processing_log.log &
Example script combinining multiple command lines.
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# Process standard variables from L2 for the 3 sensors for the year 2015
timerange_bin_map.py --aqua --terra --viirs -b 2015-01-01 -e 2015-12-31 -south 3 -north 33 -west -122 -east -72 -d /export/isilon/datos2/satmo2_data -day_vars chlor_a nflh Kd_490 sst -night_vars sst -multi 6
# Generate 8 days composites for aqua, viirs and terra for the same variables and the year 2015
timerange_time_compositing.py --aqua --terra --viirs -b 2015-01-01 -e 2015-12-31 -delta 8 -day_vars chlor_a nflh Kd_490 sst -night_vars sst -north 33 -south 3 -west -122 -east -72 -d /export/isilon/datos2/satmo2_data -multi 6
# Generate monthly composites for aqua, viirs and terra for the period 2000-2017 (for chlor_a, chl_ocx, sst and night sst)
timerange_time_compositing.py --aqua --terra --viirs -b 2015-01-01 -e 2015-12-31 -delta month -day_vars chlor_a nflh Kd_490 sst -night_vars sst -north 33 -south 3 -west -122 -east -72 -d /export/isilon/datos2/satmo2_data -multi 6